What is an ISO 80369-7 Compliant Luer? – The New Luer Standard
Luers for medical applications and the new ISO 80369 small-bore connector standards
Last updated June 15, 2021
What is ISO 80369 and how does it relate to luers?

SEGD intensive care symbol
The ISO 80369-7: Connectors for Intravascular or Hypodermic Applications standard for luer fittings is part seven of ISO 80369. ISO 80369 is a series of medical device standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization. The standards cover small-bore connectors used in the different systems providing direct, individual patient care. ISO 80369 standards were developed to significantly improve patient safety. They do this by minimizing the risk of misconnection between different fluid and gas delivery lines.
Figure 1 is the SEGD, Society for Experiential Graphic Design universal symbol for intensive care >>
The FDA has removed the December 31, 2019 deadline for no longer accepting new medical device designs for intravascular or hypodermic applications that incorporate luers that do not comply with the ISO 80369-7 standard.
This includes the removal of an October 15, 2021 compliance deadline for existing products. The FDA is currently continuing to accept ISO 594-1/-2 and ISO 80369-7:2016 as consensus standards. The FDA will issue a new deadline for conformity when the second edition of ISO 80369-7 is released.
Check out ISM’s selection of ISO 80369-7 compliant luer connector components >>
How does ISO 80369 improve patient safety?ISO 80369 applies to small-bore connectors used in medical devices or accessories intended for patient-side care. The core of these standards are new connector types that minimize the possibility of interconnections. There are ISO 80369 connector standards for each of five major types of fluid or gas delivery systems used in direct patient care. For luers, ISO 80369-7 provides revised dimensions and tolerances as well as testing procedures for confirming luers meet these standards.
The general categories of medical devices covered in the ISO 80369 standards
- Intravenous (IV) or hypodermic applications (80369-7)
- Breathing systems and gas driving applications (80369-2)
- Enteral applications such as feeding tubes (80369-3, ENFit®)
- Limb cuff inflation applications such as blood pressure cuffs (80369-5)
- Neuraxial applications such as epidural anesthesia catheters (80369-6, NRFit™)
Find out more about the ISO 80369 standard at the ISO website >>
ISO 80369-1:2018 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 1: General requirements
What is a medical device?As far as the FDA is concerned, a medical device can be as simple as a tongue depressor or a luer connector. It can also be as complex as a robotic surgical system. Medical devices even include products such as the general-purpose lab equipment used for in vitro diagnostic testing. In vitro lab testing is done in test tubes or culture dishes.
If a product is used for medical purposes and it meets the definition of a medical device it is subject to FDA medical device rules. This definition comes from section 201(h) of the Federal Food Drug and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act. FDA oversight includes both pre-market and post market regulatory controls.
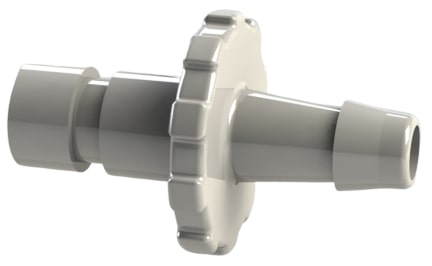
Figure 2 is a FLB7 series male luer lock by hose barb filter >>
These fittings are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
Here are two resources on the FDA website that provide some detailed background for understanding what medical devices are:
How to Determine if Your Product is a Medical Device >>
If you're enjoying what you're reading... please let us know by subscribing to our blog. You'll receive an email notification whenever we post a new article.
What are small-bore connectors?In patient care settings such as hospital bedsides and outpatient clinics, small-bore connectors and connections are used to combine the different medical devices, components and accessories of a gas or liquid delivery system. The connected parts include such things as tubing, syringes, fluid bags, gas lines, filters, backflow preventers and so on. In combination, these parts make up sub-assemblies and assemblies.
The most familiar types of assemblies are called tube sets or tubing sets. They deliver the fluids or gases needed for direct patient care. The connectors in these assemblies are called small-bore connectors because of their size. The bores or holes running through them have diameters less than 8.5 millimeters.

ISO 80369 compliant components
ISO 80369 standards minimize the chance of misconnectionsMisconnections have caused patient injuries and death in the past and represent a significant ongoing risk. This risk has been increasing over time because of the growing complexity of medical care. ISO 80369-7 Connectors for Intravascular (IV) or Hypodermic Applications applies to luer connectors and is one of these new medical small-bore connector standards intended to reduce this risk.
Up till now, luer connectors have been widely used in all sorts of medical, patient-side fluid and gas delivery systems. The new standards are intended to make luers only connectable within IV and hypodermic applications.
Figure 3 is an assortment of ISO 80369 compliant plastic connectors.
Find out more about ISO 80369-7 as an effort to improve patient safety.
Reducing Risks through Standards Development for Medical Device Connectors at the FDA website >>
Luers are a small-bore connectorLuers are one of many types of small-bore connectors. Luers are wonderfully well designed and provide an easy-to-manage, leak-free connection between a tapered male fitting and its female mating part. The luer’s design provides a friction fit that can be easily loosened and then reconnected.
Despite what you might think, the luer design is over 100 years old. It was initially developed as a connection tip for glass syringes. Because it is both leak-free and easy to use, the luer quickly became a critical low-cost component extensively used for intravascular, neuraxial, enteral, medical gas and monitoring applications.
Luers also have uses beyond medical care. They are a type of connector commonly found in modern commercial industrial applications. Uses include printer ink management, labware and lab equipment, dispensing systems and biopharmaceutical processing.
Figure 4 are a male (left) and female (right) luer thread by barb check valves >>
These check valves are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
What exactly is a luer?A luer is a standardized connection type based on a conical taper design. This taper is 6% or 1.72 degrees from the centerline. This taper is often referred to as the luer taper. Luer fittings rely on this taper and the friction between the mating surfaces to provide quick, tight, leak-proof seals between male and female luers.
The basic luer is called a slip luer or luer slip because of how the connection is made. There is also a more secure version called the luer lock. It relies on special threads to create a more secure connection that does not rely on friction alone to maintain the connection.
What is a luer lock?The luer lock was developed in 1925. Lure lock fittings have special threads added to the luer taper. Male luer locks have internal threads molded into a housing surrounding the male luer. These threads interlock with external threads or lugs added to female luer fittings.
Luer locks add mechanical strength to luer connections. They also help prevent accidental disconnections and create tighter seals. Luer lock connections are easy to take apart and secure. This is the primary reason they have become standard for syringes as well as being widely adopted for other applications.
Figure 5 is a FCV7 series male luer lock by hose barb filtered check valve >>
These check valves are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
ISO 80369 and other luer standardsThe ISO has published standards for luer fittings since 1969. The first version of these is called ISO 594-1 and it covers slip luer fittings. A related ISO standard, ISO 594-2, was issued in 1991 and it covers luer lock fittings.
ISO 80369-7 was published in October 2016 and replaces both ISO 594-1 and 594-2. The FDA has previously required that luer connectors meet the ISO 594 standards. The FDA has begun requiring medical device luers used in direct patient care comply with ISO 80369 and ISO 80369-7.
Medical device manufacturers have an ISO 80369 compliance deadline for luersAfter December 31st, 2019, the FDA no longer accepts new product submissions of medical device designs for intravascular or hypodermic applications that include luer connectors based on the older ISO 594 standards. Instead, luer connectors for these applications need to comply with ISO 80369-7 standards.
There is good news for biopharmaceutical, laboratory, chemical handling and other luer connector users. ISO 80369-7 compliant luers are designed to be backward compatible with ISO 594 luers. Keep in mind that ISO 80369-7 has replaced the ISO 594 standards for luer connectors.

The ISO 80369-7 ‘t’ dimension
An important point for all plastic luer usersThe ISO 80369-7 luer standard specifications include a particular measurement called the ‘t’ dimension. The ‘t’ dimension is from the end of the male luer tip up to the first fully formed thread.
The ‘t’ dimension was subject to interpretation in the previous ISO 594 standards for luers. The result is that you may sometimes run across fit issues between the newer ISO 80369-7 compliant luers and luers manufactured under the older ISO 594 standards.
Figure 6 is a technical drawing showing the ISO 80369-7 luer standard’s ‘t’ measurement.
Key takeaways about ISO 80369-7 and luersIf a luer connector is part of a new medical device or accessory intended for direct patient care, best practice is the luer should be compliant with ISO 80369 regardless of the connector's exact role.
These new standards provide important improvements in quality, safe patient care. Because of this, medical device manufacturers have also begun incorporating new ISO 80369-7 luers into their existing patient side medical applications.
Medical device compliance standards are a complicated subject. This article is only a very simplified introduction to ISO 80369 and the new ISO 80369-7 luer standards. It is intended for general reference purposes only. It is the responsibility of the user, designer or engineer to evaluate all components in consultation with an appropriate compliance specialist for safety and suitability of use.
Some other ISO 80369 compliant small-bore connector typesISO 80369 standards have been developed to prevent misconnection between small-bore connectors used in different applications. It ensures correct connections even in complex working environments.
Enteral feeding connector
ISO 80369-3 Enteral Feeding ConnectorsThe enteral feeding connector standard, ISO 80369-3 (ENFit®), was published July 2016.
The ISO 80369-3 standard was recognized by the FDA July 2019 >>
ENFit® is a trademark of the industry group Global Enteral Device Supplier Association (GEDSA). The ISO 80369-3 standard covers connectors for the complete enteral system, except reservoir connectors which are covered by ISO 18250-2.
Figure 7 is an ISO 80369-3 compliant enteral feeding plastic connector.
On February 11, 2015, the FDA published final guidance for small-bore connectors used in enteral applications.
Safety Considerations to Mitigate the Risks of Misconnections with Small-bore Connectors Intended for Enteral Applications guidance from the FDA for small-bore connectors used in enteral applications >>
An important note about ISO 80369-3 Enteral Feeding Connectors.
The FDA encourages manufacturers, health care professionals and hospital purchasing departments and distributors to use enteral devices with connectors that meet the ISO 80369 standard >>
More about enteral feeding (ENFit ®) connectorsENFit ® connectors are incompatible with luer connectors. They also do not interconnect with any other non-luer, non-enteral connectors used for patient side clinical applications. These include tracheostomy tubes, IV lines, limb cuff inflation lines, neuraxial lines and catheters. This fit and no-fit usability is provided by the ENFit ® connector’s larger size as well as its overall design.
What is enteral feeding?Enteral feeding usually refers to a method of feeding that delivers food or nutrition through a tube (tube feeding) that goes directly to the stomach or small intestine. People receiving enteral feeding usually have some sort of medical condition or injury that prevents them from eating their regular food.
Enteral feeding is usually a practical option in cases where someone's digestive system (GI tract) is still working just fine. In fact, a benefit of enteral feeding in these cases is that it helps keep their GI tract working properly. Enteral feeding can provide for a person's entire caloric needs or it may be used to provide supplementary nutrition.
Find out more about the ISO 80369-3 standard for enteral feeding connectors at the ISO website >>
ISO 80369-3:2016 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications
Limb cuff by barb connector
ISO 80369-5 Limb Cuff ConnectorsThe ISO 80369-5 standard for limb cuff inflation application small-bore connectors was originally approved and published March 2016. This standard is based on a bayonet style connection.
The ISO 80369-5 standard was recognized by the FDA August 2017 >>
Figure 8 is an ISO 80369-5 compliant blood pressure limb cuff bayonet by hose barb plastic connector.
What applications use limb cuff inflation?Limb cuff inflation applications include blood pressure cuffs, tourniquet cuffs and surgical tourniquets. The new ISO 80369 worldwide standard for these bayonet-style connectors does not allow interconnection with either luer or other, non-luer connectors used for patient-side clinical applications. This fit and no-fit usability is provided by the bayonet-style design of the connectors.
Like the other ISO 80369 standards, ISO 80369-5 significantly reduces the risk of dangerous and potentially fatal misconnections.
Find out more about the ISO 80369 standard for limb cuff inflation connectors at the ISO website >>
IEC 80369-5:2016 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 5: Connectors for limb cuff inflation applications

Neuraxial connectors
ISO 80369-6 Neuraxial ConnectorsThe ISO 80369-6 (NRFit™) standard for neuraxial application small-bore connectors was originally approved and published March, 2016. NRFit™ is a trademark of the Global Enteral Device Supplier Association (GEDSA).
The ISO 80369-6 standard was recognized by the FDA June 2016 >>
Figure 9 are female (top) and male (bottom) ISO 80369-7 compliant neuraxial plastic connectors.
More about neuraxial (NRFit™) connectorsNRFit™ connectors have unique design features that dramatically reduce the risk of cross-connections with both luer connectors and non-luer, non-neuraxial connectors. Non-neuraxial patient-side applications may include tracheostomy tubes, IV lines, limb cuff inflation lines, neuraxial lines and catheters. The fit and no-fit usability is provided by the NRFit ® connector’s smaller size, 20% smaller than luer connectors, in combination with other design features.
What applications use neuraxial connectors?Applications that require neuraxial connectors include spinal anesthesia, intrathecal chemotherapy, lumbar puncture, cerebrospinal fluid collection and pressure measurement, epidural catheter placement with bolus injection and major regional anesthesia.
Find out more about the ISO 80369 standard for neuraxial connectors at the ISO website >>
ISO 80369-6:2016 Small bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 6: Connectors for neuraxial applications
Figure 10
Female luer lock by barb connector
Figure 10 is an CFL7 series female luer lock or thread by hose barb plastic connector >>
These fittings are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
A list of references mentioned in this post
Various reference links
- ISO 80369-7 Luer standard: What this means for plastic luer users at MPN, Medical Plastics News >>
- SEGD – The Society for Experiential Graphic Design About Us page >>
FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration)
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recognition of the ISO 80369-3 (ENFit®) standard July 2019 at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recognition of the ISO 80369-5 standard August 2017 at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recognition of the ISO 80369-6 (NRFit™) standard June 2016 at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recognition of the ISO 80369-7 (2nd edition 2021) December 2020 at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
Figure 11
Male luer lock by barb connector
Figure 11 is a CIML7 series male luer lock by hose barb plastic connector >>
These fittings are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
- How to Determine if Your Product is a Medical Device at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- Medical Device Connectors at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
This page contains a link to the September 7th, 2018 letter from the FDA encouraging the use of ISO 80369-3 (ENFit®) enteral connectors.
- Medical Device Overview at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- Quality and Compliance (Medical Devices) at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
- Reducing Risks through Standards Development for Medical Device Connectors at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website >>
Figure 12
Male luer lock by bond in port connector
Figure 12 is a BNP7 series male luer lock by bond-in port fitting plastic connector >>
These fittings are ISO 80369-7 compliant for intravascular (IV) applications.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- ISO 80369-1:2018 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 1: General requirements >>
- ISO 80369-3:2016 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 3: Connectors for enteral applications >>
- IEC 80369-5:2016 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 5: Connectors for limb cuff inflation applications >>
- ISO 80369-6:2016 Small bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 6: Connectors for neuraxial applications >>
- ISO 80369-7:2016 Small-bore connectors for liquids and gases in healthcare applications — Part 7: Connectors for intravascular or hypodermic applications >>
If you found this article useful... please consider subscribing to our blog. You'll receive an email notification whenever we post a new article.
« Go back to the blog homepage